Abstract
Pedestrian crossings serve as crucial components of urban infrastructure, ensuring the safe traversal of pedestrians across busy streets. While some crossings are equipped with timed signals and supplemented with signage and lights, others rely solely on road markings. However, these markings are susceptible to wear and tear from various factors such as traffic, weather, and maintenance activities, potentially compromising road safety by diminishing their visibility to drivers. This paper presents a comprehensive study on employing computer vision techniques for the identification and classification of pedestrian crossings.
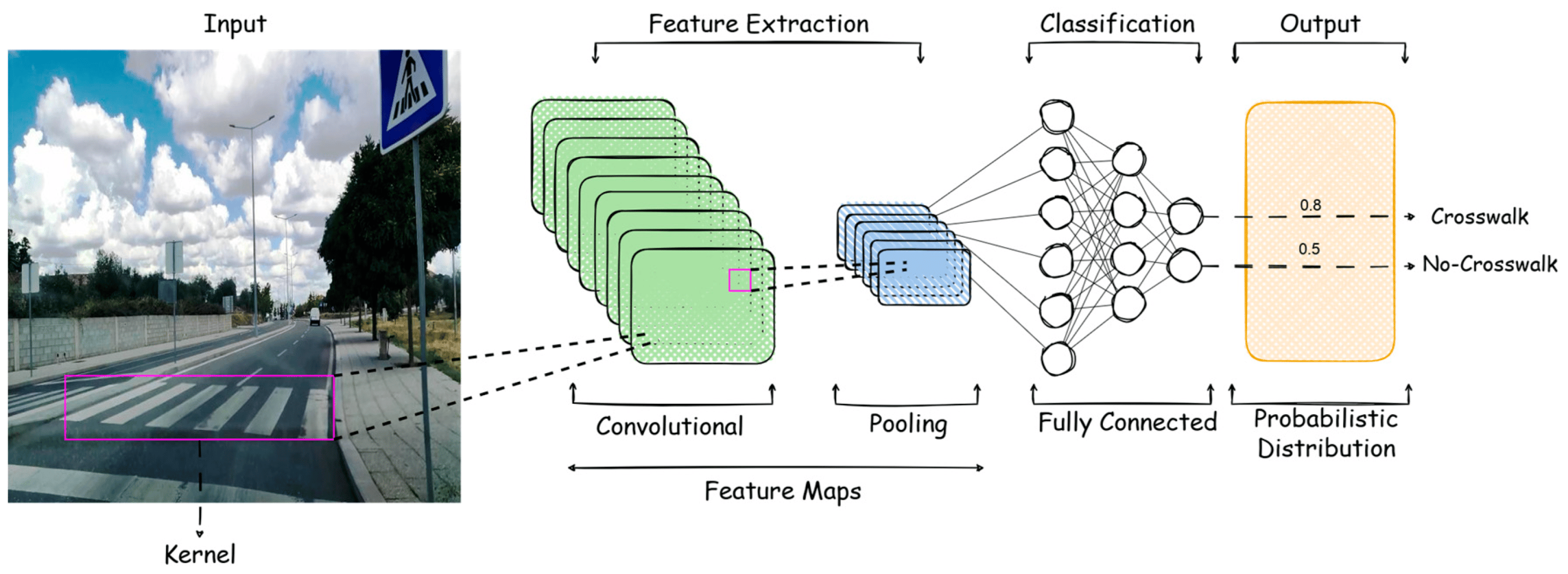
The study begins by elucidating pertinent concepts surrounding pedestrian crossings. It subsequently conducts a survey of existing literature, categorizing and analyzing prevalent solutions while delineating their respective strengths and limitations. The focal point is the exploration of several promising computer vision techniques, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG), Maximally Stable Extremal Regions (MSER), Canny Edge detection, and thresholding methods.
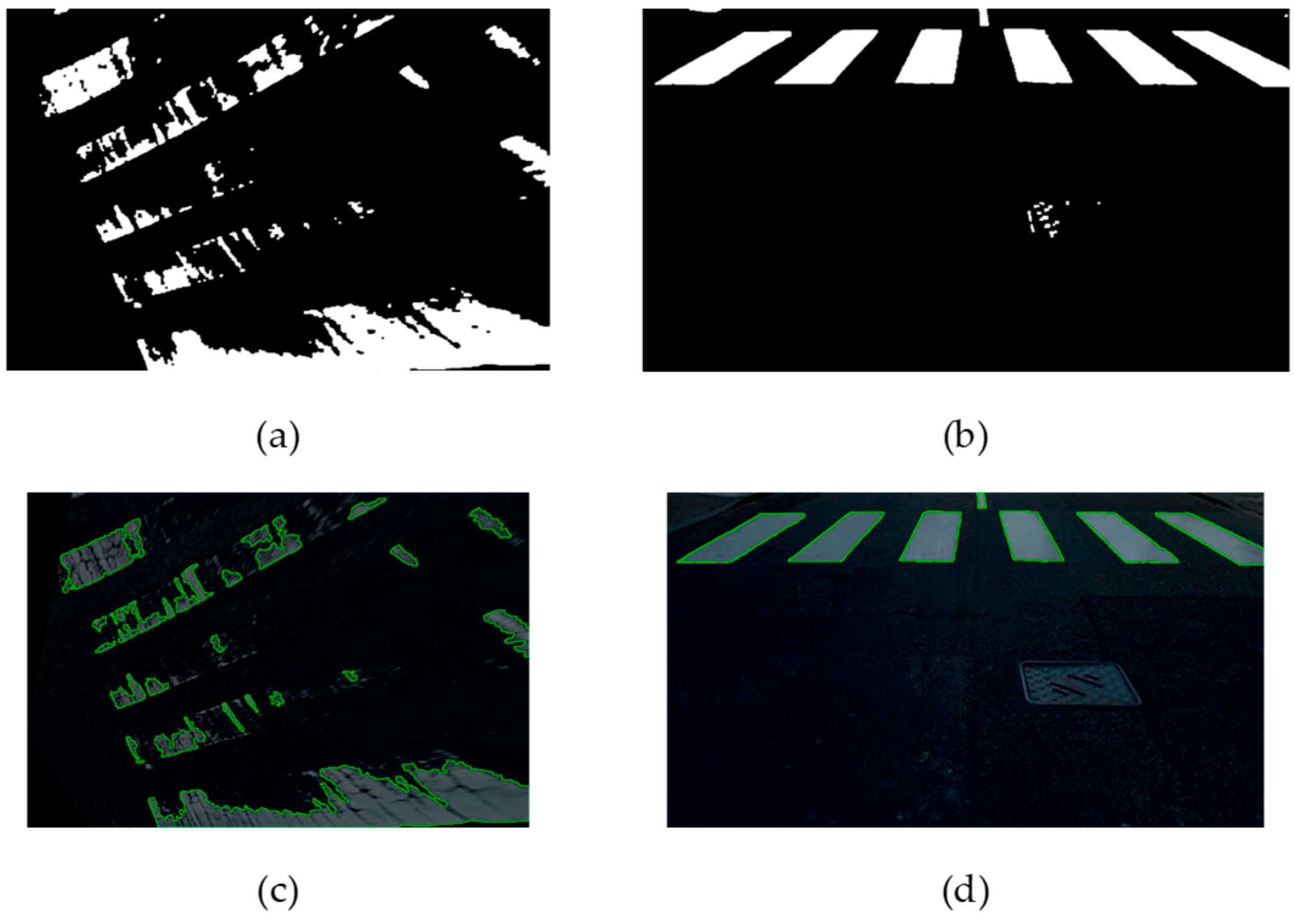
Furthermore, the paper undertakes an evaluation and comparison of these techniques utilizing a bespoke dataset crafted specifically for this research endeavor. Through this analysis, valuable insights are gleaned regarding the performance and efficacy of each approach. Notably, the findings underscore the potential of computer vision methodologies in facilitating the automation of pedestrian crossing assessment, particularly in the context of smart city initiatives aimed at enhancing road safety.
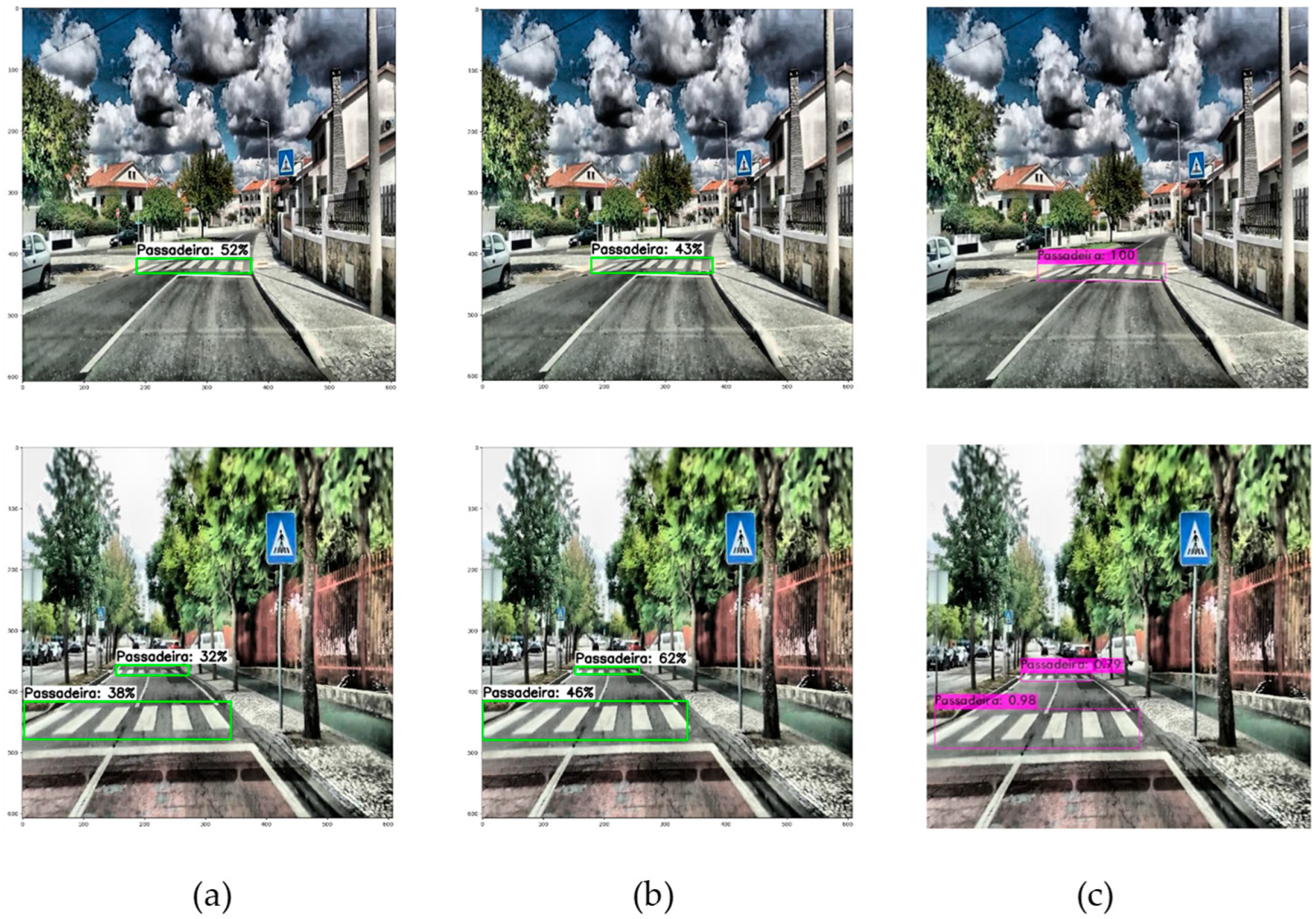
In conclusion, this study not only provides a comprehensive overview of computer vision techniques for pedestrian crossing detection but also sheds light on emerging research avenues and unresolved challenges in the domain. Ultimately, it advocates for the adoption of such technologies by road safety managers to streamline the monitoring and maintenance of pedestrian crossings, thereby contributing to the realization of safer urban environments.
Gonçalo J. M. Rosa, João M. S. Afonso, Vasco N. G. J. Soares, João M. L. P. Caldeira, Pedro D. Gaspar